A powerful hybrid physical modeling virtual instrument.
Your portal to new sound universes inspired from the real world, where objects collide, vibrate, and resonate.

Try the demo
Fully functional, no time limit, 30-second silence every 10 minutes
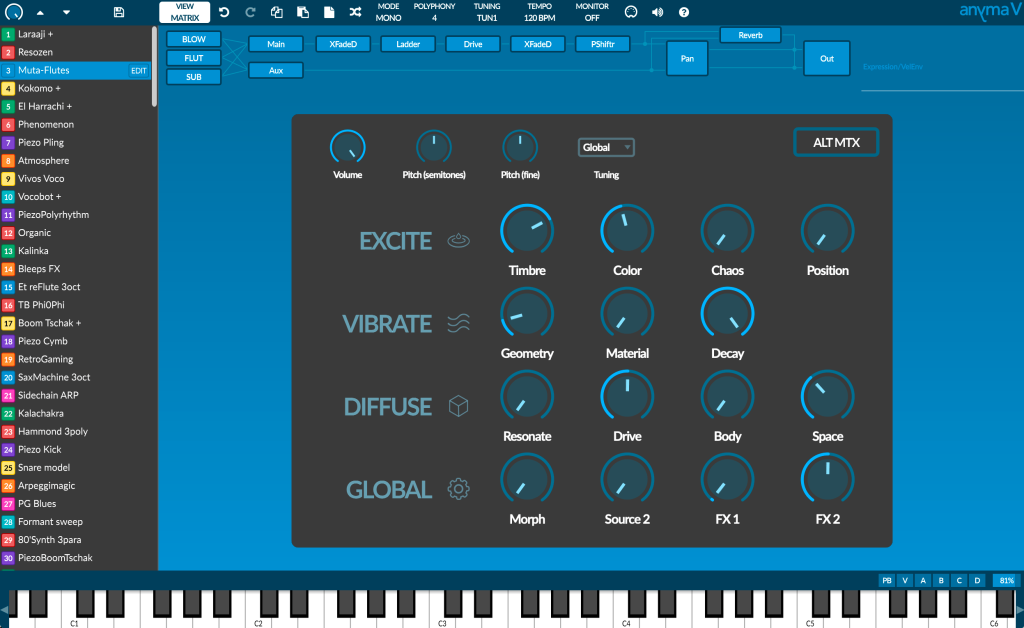
Hybrid polyphonic synthesizer
The best of both worlds
Anyma V blends the classic ingredients of electronic music, like oscillators and filters, with physical modeling technology, allowing it to simulate acoustic sound sources, such as strings or reeds, as well as resonating structures, like wood, glass, or metal. It can also add physical behaviors to modulations, like bouncing balls and springs.
A virtual Anyma Phi
Hardware origins
As the virtual counterpart to the Anyma Phi hardware synthesizer, Anyma V shares the same sound engine and patch format, enabling seamless patch creation and transfer between both instruments. Unlike its hardware sibling, Anyma V offers polyphonic capabilities and unlimited instances in your DAW.

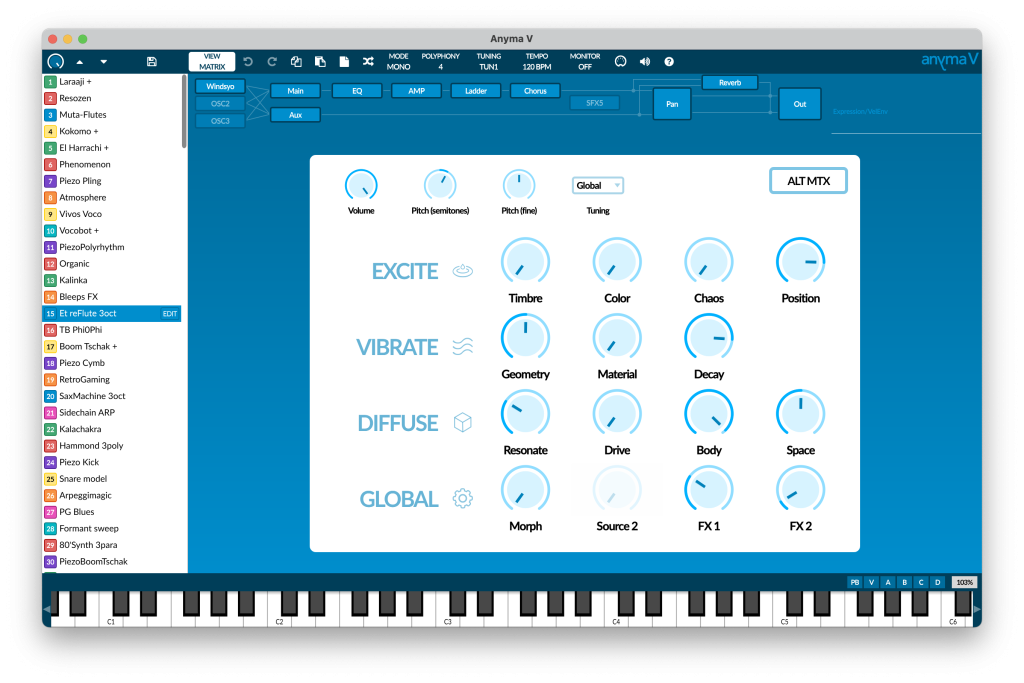
Create unique sounds
Sound design for all
The matrix provides a quick and easy way to explore your sounds by following a physical metaphor, with four sections for each stage of sound generation: Excite, Vibrate, Resonate, and Global. Using Morph, you can transition seamlessly between two versions of the matrix.
Infinite possibilities
A semi-modular powerhouse
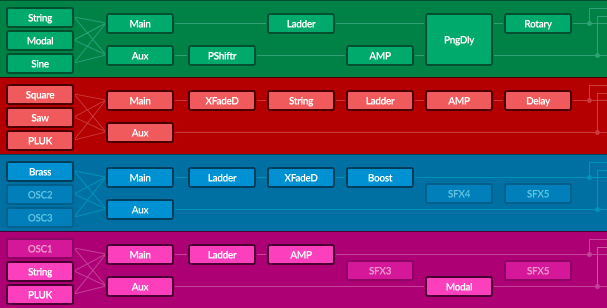
Beyond the matrix lies an insanely powerful semi-modular synthesis engine where you can harness a wide variety of oscillators and effects, and control them effortlessly using an impressive modulator system. Everything is under your control, on a single screen.
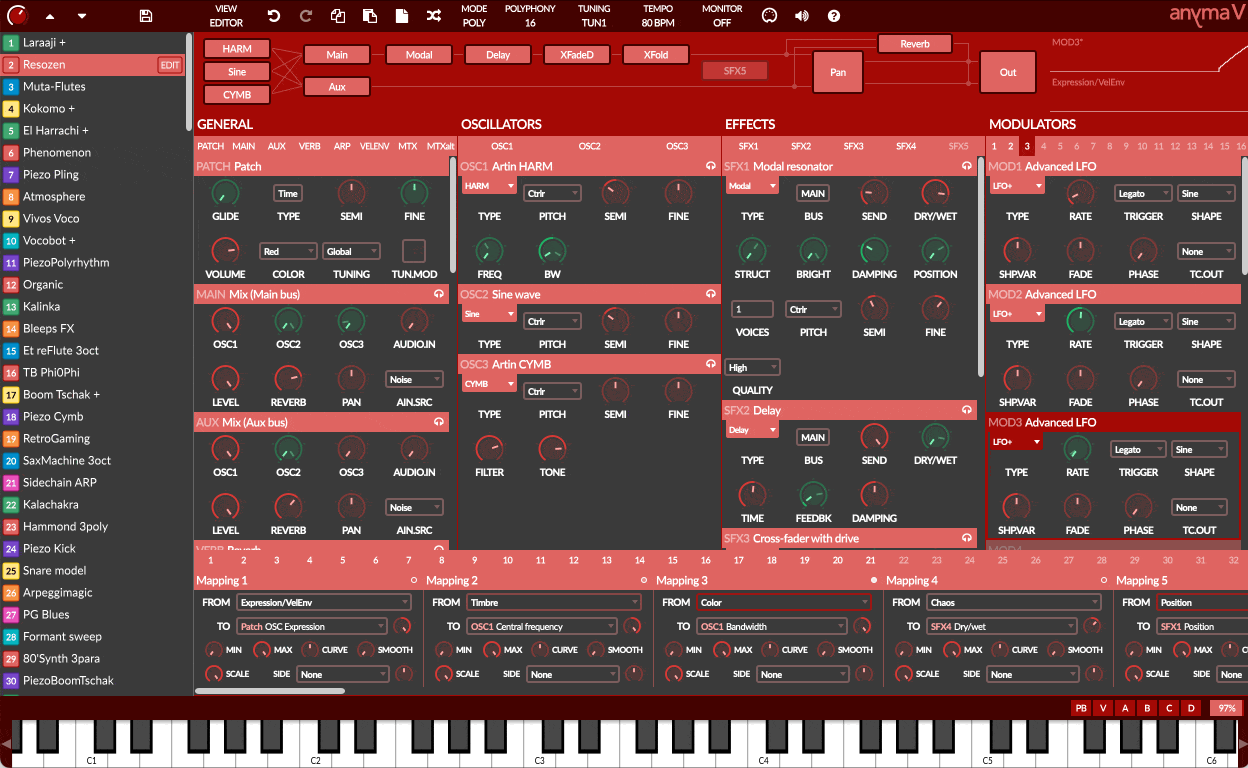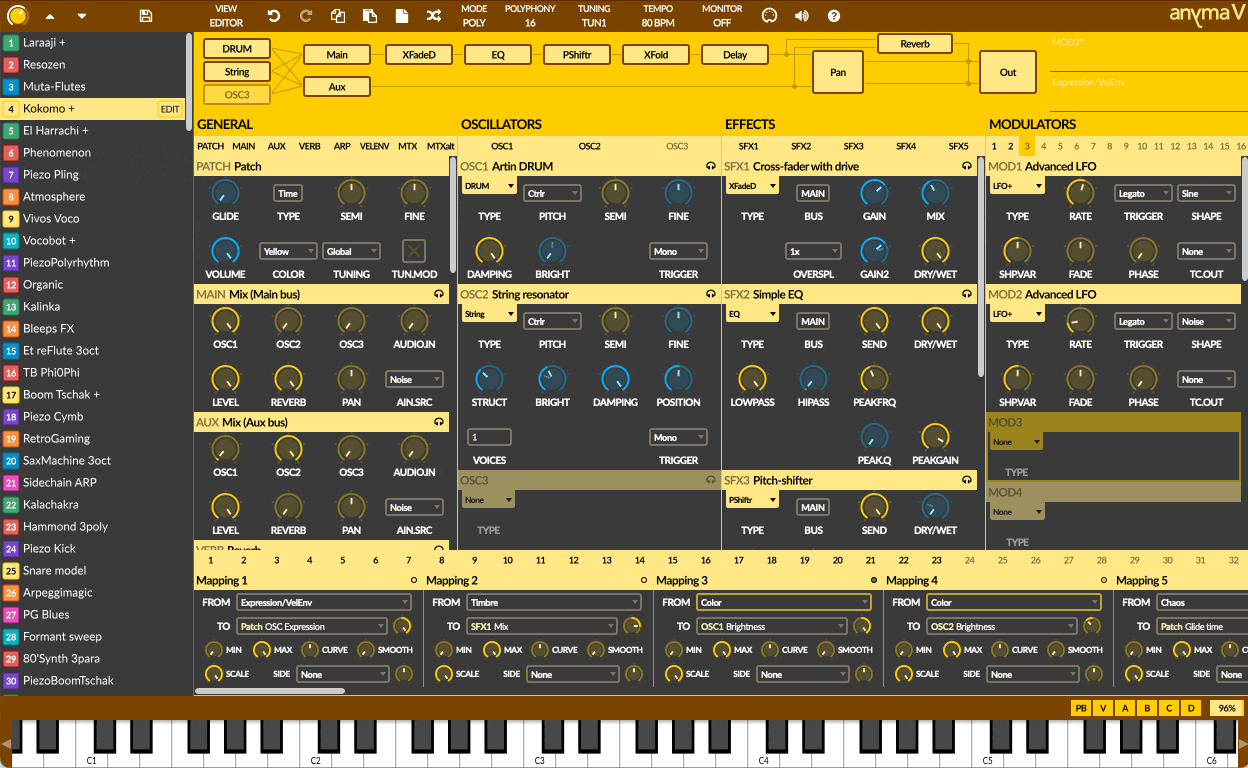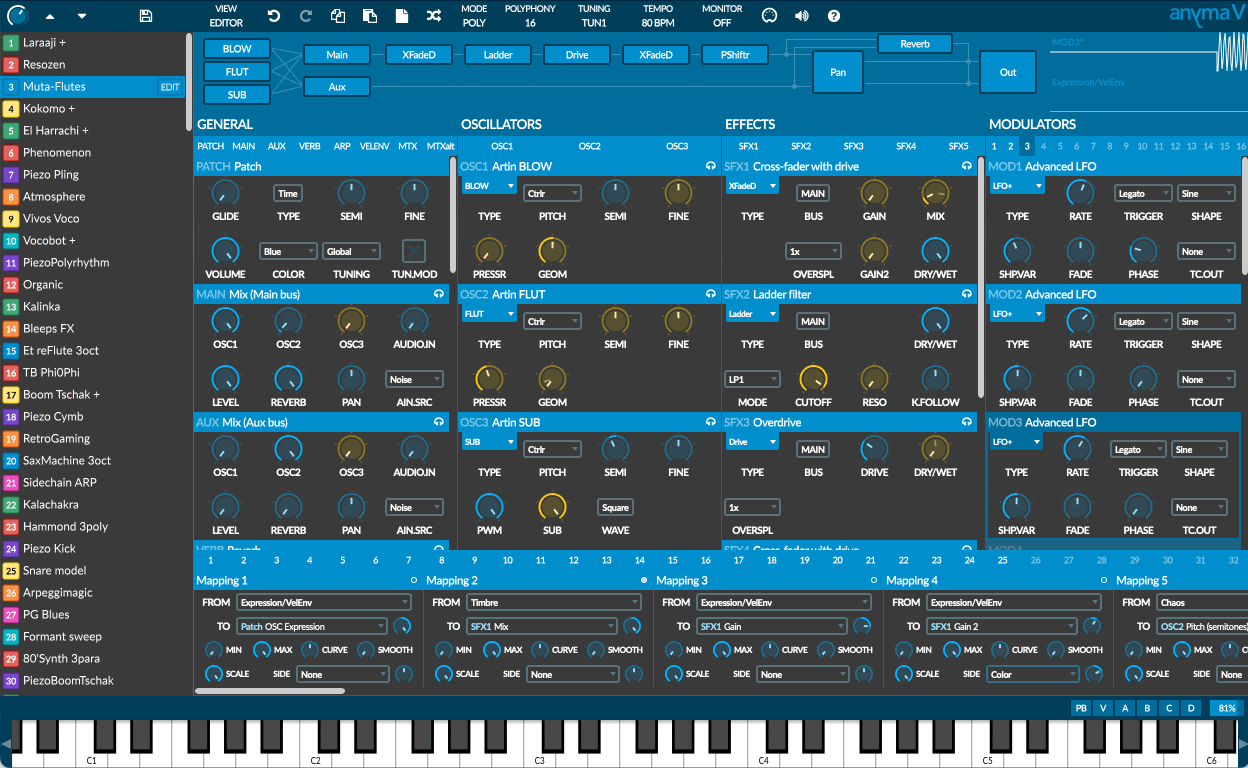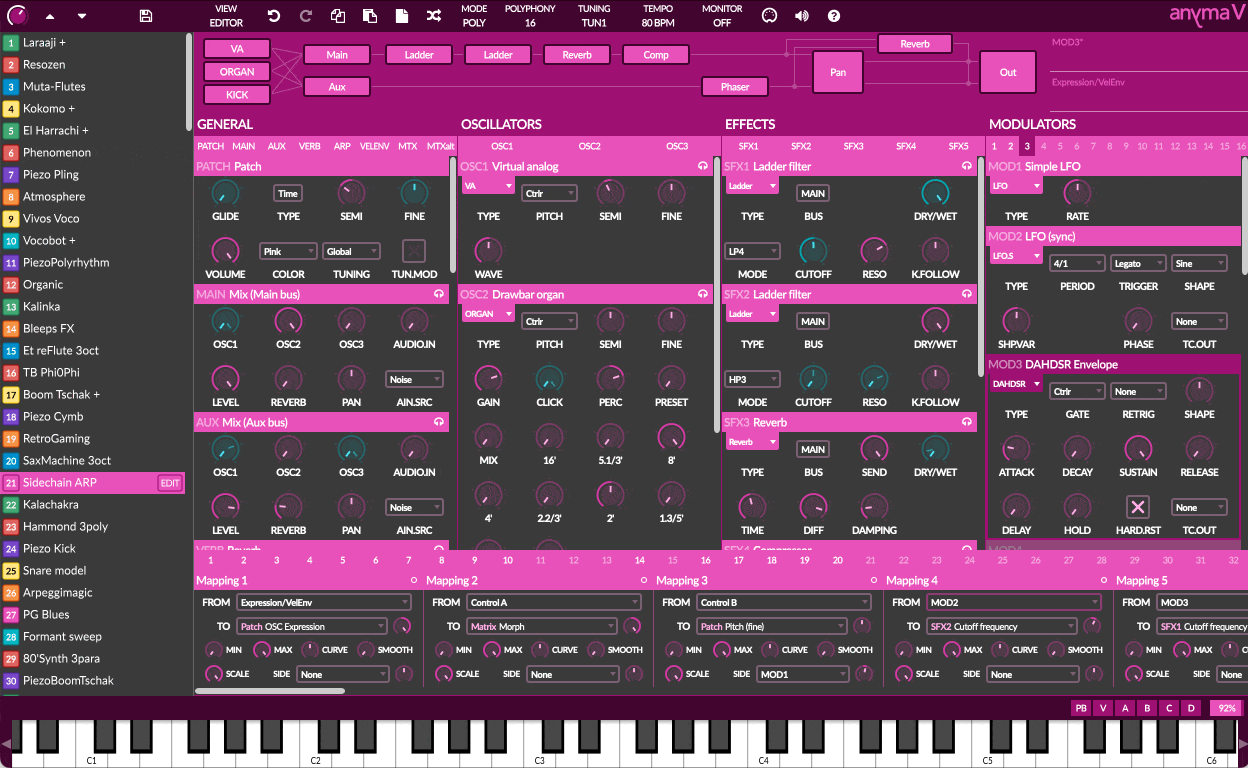
54 OSCILLATOR MODULES
36 EFFECT MODULES
47 MODULATOR MODULES
MIDI MPE compatible
In tune with its environment
Anyma V is compatible with any MIDI controller, such as keyboards, sequencers, or even wind controllers, including our own Sylphyo. In addition, it supports MPE controllers and DAWs, allowing you total freedom in how you control your sound. You can easily adjust mappings, mono/poly mode, and tempo, with internal and external sources.
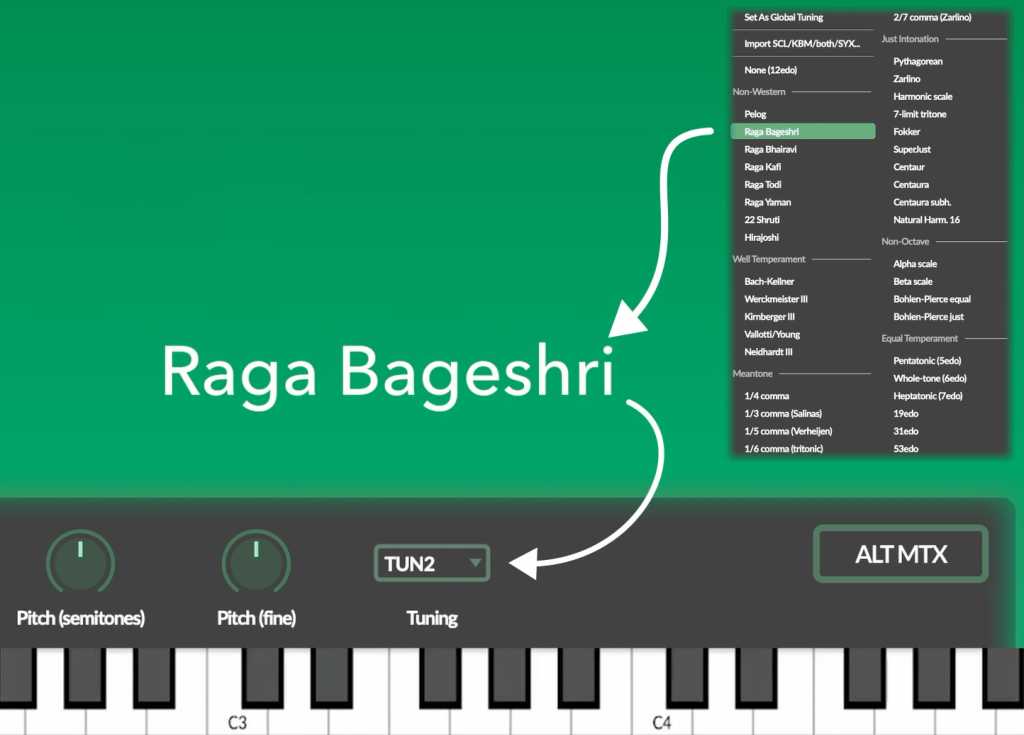
Tuning and microtonality
Beyond semitones
You can tune Anyma V to any reference frequency or tuning system, such as just intonation, historic or non‐Western tunings, or those of modern microtonal and xenharmonic music.
Aside from the more than 30 preset tunings, you can also import Scala and MTS SysEx files.
Discover the versatile sonic
capabilities of Anyma V
Try the demo
Minimum requirements
Windows
- Processor: Intel/AMD (32‐bit or 64‐bit) or ARM 64‐bit processor
- RAM: 1 GB of RAM
- Disk space: 100 MB of free disk space
- Operating system: Windows 7 or more recent
- Formats: Standalone, VST3 plugin
macOS
- Processor: Intel 64‐bit or Apple Silicon processor
- RAM: 1 GB of RAM
- Disk space: 100 MB of free disk space
- Operating system: OS X 10.9 or more recent
- Formats: Standalone, Audio Unit and VST3 plugins
Linux (limited support)
- Processor: Intel/AMD 64‐bit or ARM (32‐bit armv7hf or 64‐bit armv8) processor
- RAM: 1 GB of RAM
- Disk space: 100 MB of free disk space
- Operating system: Any OS with Linux 3.2.0 kernel or more recent and glibc
- Formats: Standalone, VST3 plugin
Aodyo Community
A caring community to help you stay on track.
The Aodyo Community is a place where members can share their ideas, sounds & patchs, ask questions, get involved in helping people as well as much more.
Full module list
OSCILLATORS
Exciters
Bow (Bowing noise generator)
Wind (Wind noise generator)
Strike (Percussive noise generator)
Noise
White noise (A simple white noise generator)
Artin NOIS (Filtered noise)
Artin TWNQ (Resonant noise)
Artin CLKN (Random sample generator)
Artin CLOU (Granular cloud generator)
Artin PRTC (Particle system simulator)
Artin QPSK (Telecommunication data generator)
Artin TOY (Circuit-bent toy)
Physical modeling
Modal resonator (Vibrating structure simulator)
String resonator (Vibrating string simulator)
Windsyo (Complex reed-based physical models)
Brass (Brass physical model)
Artin PLUK (Simple plucked string)
Artin BOWD (Simple bowed string)
Artin BLOW (Simple single-reed wind)
Artin FLUT (Simple flute)
Drawbar organ (Classic drawbar organ sound)
Free Reed (Free-reed aerophone model)
Percussive
Artin BELL (Additive bell sound synthesizer)
Artin DRUM (Additive metal drum synthesizer)
Artin KICK (808-style kick drum)
Artin CYMB (808-style cymbal)
Artin SNAR (808-style snare drum)
Analog
Sine wave (Pure tone without any harmonics)
Triangle wave (Soft tone with some odd harmonics)
Square wave (Harsh, rich tone with many odd harmonics)
Sawtooth wave (Very rich tone with many harmonics)
Virtual analog (A virtual analog oscillator with smooth waveform transition)
Artin SUB (Waveform with sub-oscillator)
Artin CSAW (CS-80 style sawtooth with variable notch)
Artin MORPH (Kobol-style variable waveform: triangle, sawtooth, square, pulse)
Artin SAWSQR (Blends sawtooth and square wave)
Artin FOLD (Folded sine/triangle)
Artin SYNC (Dual hard-synced waveforms)
Artin X3 (Triple oscillator)
Artin SAWSWARM (Seven detuned sawtooths)
Artin SAWCOMB (Sawtooth and tuned comb filter)
Digital
Artin BUZZ (One to many sine waves)
Artin VOSM (Voice simulator)
Artin VOWL (Early speech synthesizer)
Artin VFOF (FoF vowel simulator)
Artin HARM (Additive synthesizer)
Artin FM (Two-operator Sine FM synthesizer)
Saw FM (Two-operator Saw FM synthesiser)
Artin ZPDF (CZ-style phase-distorted waveform)
Wavetable
Artin WTBL (Wavetable synthesizer)
Artin WMAP (2D wavetable synthesizer)
Artin WLIN (Interpolated wavetable synthesizer)
Artin WTx4 (Four-voice wavetable synthesizer)
Paraphony
Replicant (A copy of the previous oscillator)
EFFECTS
Physical modeling
Modal resonator (Vibrating structure simulator)
String resonator (Vibrating string)
Snare drum (A physical model of a snare drum)
Dirty formant filter (Old-school FoF-based formant filter)
Comb filter (Old-school comb filter)
Filter bank (A bank of four band-pass filters)
Filter
State-variable filter (Two-stage resonant filter)
Ladder filter (Four-stage resonant filter)
Simple EQ (Equalizer)
Dynamics
VCA (Voltage-controlled amplifier)
Tremolo (Change the amplitude of the input in a periodic way)
Noise gate (Attenuates the input when the signal is below a threshold)
Compressor (Compress the input signal)
Dynamics booster (Tame or boost the signal by compressing it)
Mix
Cross-fader (Balances between two inputs)
Cross-fader with drive
Rotary speaker (stereo)
Timbre
Amplifier (A saturating amplifier)
Overdrive (Saturates without increasing volume)
Bitcrusher (Reduces the resolution of the audio signal)
Cross-modulation
Cross-folder (Wavefolds two inputs together)
Ring modulator (Ring-modulates two inputs together)
XOR modulator (XORs two inputs together bit by bit)
CMP modulator (Cross-modulates two inputs with digital comparison operators)
Modulation
Chorus (Thickens the input)
Phaser (Six-stage phase shifter)
Pitch-shifter (Transposes the input)
Rotary speaker (Simulation of a rotary speaker)
FM Operator (An oscillator that can be used to build complex FM structures)
Delay
Delay (Delay line with feedback and damping)
Delay (sync)
Ping-pong delay
Ping-pong delay (sync)
Reverb (Mono reverberation effect)
Granular processor (Creates audio textures by combining short segments of the input)
MODULATORS
LFO
Simple LFO
Advanced LFO (Advanced low-frequency oscillator with shape and fade-in controls)
Slow LFO (Low-frequency oscillator with very long periods of time)
LFO (sync) (Low-frequency oscillator synced to the tempo)
Envelope
Envelope (Simple envelope generator)
DAHDSR Envelope (DAHDSR envelope generator)
Sequencer
Step sequencer (Change a value according to a predetermined pattern over time)
Euclidean sequencer (Generate euclidean rhythms)
Hex sequencer (Generate rhythms from hexadecimal numbers)
Audio
Envelope follower (Transform an audio signal into a smoothed value)
Timbre follower (Extract the brightness from an audio signal)
Drum trigger (Derive a signal suitable for percussive sound triggering)
Shape
Xform (General-purpose value transform)
Curve (Apply a curve to a value)
Quantize (Reduce the resolution of a value)
Change polarity (Make a unipolar value bipolar, and vice-versa)
Smooth (Smooth out the variations of a value)
Accumulate (Accumulate a value or variations over time)
Lookup table (Change a value according to a predetermined shape)
Physics
Bouncing ball (Simulate the movement of a single bouncing ball)
Ball impact (Simulate the impact of several independent bouncing balls)
Spring-damper system (Simulate a spring-damper system attached to the input)
Chaos
Logistic map (Unfold the logistic equation on each trigger)
Tent map (Unfold the tent map sequence on each trigger)
Circle map (Unfold Arnold’s circle map sequence on each trigger)
Discrete chaotic map (Apply a specific chaotic map equation on each trigger)
Cellular automaton (Use specific bits of a running cellular automaton)
Logic
Gate combinator (Perform successive operations on a series of gates)
Trigger combinator (Perform successive operations on a series of triggers)
Gate to trigger (Converts gate transitions into triggers)
Gate delay (Delay the gate signal by a given time offset)
Trigger delay (Delay the trigger signal by a given time offset)
React
Impulse (Generate an impulse from a value and a trigger)
Count (Count occurrences of a trigger)
Time (Measure the time since a trigger)
Delay (Delay the signal by a given time offset)
Latch (Capture a value when a trigger occurs)
Minimum (Keep the minimum of a value since a trigger)
Maximum (Keep the maximum of a value since a trigger)
Compare (Determine when the input value goes above or below a threshold)
Constrain
Clamp (Limit a value to an interval)
Wrap (Wrap a value around an interval)
Fold (Fold a value inside an interval)
Combine
Interpolate (Cross-fade between two values)
Interpolate (4-point) (Interpolate between four points)
Calculate (Perform successive operations on a series of values)
The items marked Artin, as well as a few others, are rewrites or adaptations inspired from Emilie Gillet’s fantastic work on Mutable Instruments modules.


 No products in the cart.
No products in the cart.